| Law | Symbolic Representation | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Commutative Law | The order of applying the operation does not affect the result. | |
| Associative Law | The grouping of operands does not affect the result. | |
| Closure Law | The result of applying the operation to two elements from a set is still an element of that set. |
a)Closure
Supplementary angles: whose sum is 180(degree)
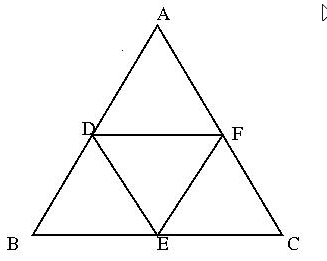
- ratio of area of ABC to DEF= 1/4
- perimeter of ABC to DEF = 1/2
- measure of angles of DEF= 60º
- all triangles are congruent
- ratio of length of AC to DE = 1/2
- CDEF forms a rhombus
Part 1
1: Number System -+
; ;
a)
- when solving
you can make it simpler by doing
a)
m
-
Modulus or Absolute value=
= -
argument =
-
theorem for complex numbers also called polar forms are:
- De-moivre's:
- Euler formula:
- De-moivre's:
-
polar co-ordinates of a point
-
-
-
a)
- multiplication of complex numbers
-
field of rational numbers
is field of complex numbers -
-
Inverse of
is:
MCQ -
Multiplicative Inverse: when multiplied turns the number into 1
Additive Inverse: When added turns the number into 0
a)0
a)(3, 0)
2: Sets and Sub-Sets -+
- Power of a Set = No. of subsets =
- Absorption Law:
-
; all the elements that are not in A -
A\B =
where A\B means all that elements that are in A but not in B -
-
there is only one inverse for each element in a set/group
| Converse | ||
| Inverse | ||
| Contra positive |
- if function's elements are in sets of ordered pairs swapping their position is the function's inverse
- Groupoid: if elements are closed with respect to an operator(closure property)
Semi Group: groupoid but order when applying operator doesn't affect the result(associative property)- order of a group is its number of elements
| Name | Notation | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Subset | A ⊆ B | all elements of A are in B |
| Superset | B ⊃ A | B has every element of A(basically A is subset of B) |
- if
is a set, represents the number of elements in
3: Matrices -+
- Minor
: determinant of matrix after removing row and column - Co factor
- Symmetric:
Skew-Symmetric - Order: Row x Column
for all square matrices where is the order of the matrix - if a whole row/column is zero, determinant is zero
if a two whole rows or columns are equal then determinant is zero if - if A is diagonal matrix, then its inverse is reciprocal of its elements i.e
- if A is diagonal then its determinant |A| is simple product of diagonal elements.i.e
- solve determinant of
or higher using determinant properties
a)6
4: Quadratic Equations
- Fourth roots of 16 are:
- sum of fourth roots is zero
- A quadratic has a degree of 2, always
- if
is root of polynomial equation then is zero
a)1
- at the point of intersection of two rays their functions are equal.
- for
whose roots are then $$\begin{align*} S = \alpha + \beta &= -\dfrac{b}{a} \ P = \alpha \times \beta &= \dfrac{c}{a} \ \ ax^2 + bx + c &= x^2 - Sx + P \end{align*}$$
a)
since
- In a homogeneous system, if the determinant of the coefficient matrix is non-zero, the system only has trivial solution (i.e.
a)Trivial Solution
since
6: Sequences and Series+
\hline
\textbf{Type} & \textbf{General Term} & \textbf{Sum} & \textbf{Mean} & \textbf{Example} \
\hline
\text{A.P.} & a_n = a + (n-1)d & S_n = \dfrac{n}{2}[2a_{1} + (n-1)d] = \dfrac{n}{2}(a_{1} + a_n) & \text{A.M} = \dfrac{a + b}{2} & 2, 5, 8 \
\hline
\text{G.P.} & a_n = ar^{n-1} & S_n = \dfrac{a_{1}(1 - r^n)}{1 - r} , \text{for} , r < 1, , \text{or} , S_n = \dfrac{a_{1}(r^n - 1)}{r - 1} , \text{for} , r> 1 & \text{G.M} = \sqrt{ab} & 3, 6, 12 \
\hline
\text{H.P.} & a_n = \dfrac{1}{a + (n-1)d} & S_n = \dfrac{n}{\dfrac{1}{a_1} + \dfrac{1}{a_2} + \dots + \dfrac{1}{a_n}} & \text{H.M} = \dfrac{2ab}{a+B} & 1, \dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{1}{3} \
\hline
\end
- for two terms in GP
and
e.g.
- find any
from any with
e.g.
a) 1536
- term of GP remain in GP even after reciprocal
7: Permutation and Combination +
- permutation: different arrangements of n numbers taken r at a time
Combination: selection of r objects from a total of n objects, where the order of selection does not matter.
- if in combination or permutation q* objects are always included:
or if never included or
- if some object in permutation is being repeated say
times e.g. A,B,B,C,C,C,D (B is repeated 2 times and C 3 times so) then its permutation taking 5 at a time is
a)72
and
a)360
also try for corporation , note that
a)5
since divisible by 5, 5 is fixed at the end, no digits repeat so
a)320
a)242
less than a lakh has 5 digits, each digit can be replaced by 3 possible numbers so
excluding 00000, so 243-1=242
-
Diagonals in an
sided polygon: -
circular permutation =
circular permutation on a flipable ring = -
common factorials
| 0! | 1! | 2! | 3! | 4! | 5! | 6! | 7! |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 24 | 120 | 720 | 5040 |
- in permutation order of elements matters while in combination only the presence of an elements matters
- how to determine whether the question requires permutation or combinations
Combination:
a)5
- for consecutive
's with same n: keeping the larger
a)Both B and C
solution:
and using above given rule, 8 is higher so we
a)none
are equal for all n and m, if as
Geometrical problems
- if n is the number of non-collinear points
a)28
a)40
| Pecrmutation | Combinations |
|---|---|
| Arrangements standing or sitting in row or in a circle problem regarding digits letters(A,B,C...) Formation of words, number,etc |
Selection, Choice, Draw,etc Distributation, formation of a group, commitee, team,etc problem regarding geometry |
Probability:
- Rules of probability:
- Probability of an event =
- Probability of an event =
a)
- blueeeeh:
- probability can never be greater than 1
- Improbability of an event =
a)
Total outcomes:
| Die | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
a)
- Card in a deck:
- Spades, Hearts, Diamonds, Clubs:
- Black Cards: 26, Red Cards: 26
- Face Cards:
- All Hearts and Diamonds are Red
- All Spades and Clubs are Black
- Spades, Hearts, Diamonds, Clubs:
a)
Red card Prob:
- 1/2 Probability of even and odd sum from one or multiple dice rolls
- possible outcomes of an experiment with
outcomes performed times: , then probability is - Possible outcomes of a coin tossed
times: - Possible outcomes of a dice rolled
times:
- Possible outcomes of a coin tossed
a)
a)
Total outcomes:
- probability of an
- dependent events:
a work is to be and involves 3 steps, step 1 has probability of completion 0.7, step 2 has probability of completion 0.8, step 3 has probability of completion 0.9, total probability of work being done is?
simply multiply them
8: Mathematical Induction and Binomial Theorem
Mathematical Induction
- Use back solving method
a)
since n is a natural number, using 2 and adding only first two numbers (1+2) = 3, now put n=2 in each option and whichever equal 3 is correct
a)7
a)
since
Binomial Theorem
where
a)
since there are alternating minus sign, A contain a minus, and 2nd term is 8x, which is n(
- number of terms is
a)5
first make it binomial and it becomes
-
Middle term if n is even:
position -
if n is odd:
position -
Sum of binomial co-efficient:
-
Sum of even or odd binomial co-efficient:
a)7
since
- Find Sum of co-efficient
of by replacing by 1 and solving
a)32
- Sum of exponent of
and in each term is equal to
a)
term or power of b:
a)
b) c) d)
8th term so r=7, since all coefficient same in option, don't need to calculate
- if asked to find Xth terms from last, simply exchange
and :
a)
this time we calculate the combination,
- Term involving Cth power of x as
in an equation of form : we get value of r by doing where t is the combined degree of and here its 2 it is simply nth position, if has a degree of 1 - term independent of
means , where c=0
a)
here
9-14: Trigonometry
9: Fundamentals of Trigonometry
| System | units | conversion | definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| sexagesimal | 1 degree is the angle, the 360th part of a circle subtends on the centre | ||
| circular | rad. | the angle subtended by an arc equal in length to radius |
-
basic unit of angle is second (60th part of a minute and 3600th part of a degree
-
Calculate angle between clock hands:
a) 275
275 is in 4th quad so (360-275) = 85 so both
| Polygon | Area | Perimeter | arc |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circle | |||
| Sector | |||
| Triangle | |||
| 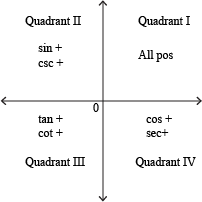 |
| co-ratios | Identity | addition | double angle | triple angle | half angle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sin |
Cos |
|||||
| Cos |
Sin |
|||||
| Tan |
Cot |
irrelevant | irrelevant | |||
| Sec |
Cosec |
|||||
- if sum of two angles is 90 then those co ratios are equal
a)
a)0
a)
simplify put t=90 and compare answers with each option
a)0.2
a)2
- for a right angled triangle
since 71+19= 90, so tan 71 = Cot(90 - 71) = Cot 19
and tan 45 and cot 45 both equal to one
- Allied angle concept: if
ifis odd, then the function applied on is converted to it co-ratio with angle , otherwise remains same
if the function atis negative, then has a negative sign
e.g.since is negative in 2nd quad - for a right angled triangle
| product to sum/diff | Sum/diff to product | |
|---|---|---|
| sin | ||
| cos | ||
| function | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||||
| 0 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | undefined |
10: Trigonometric Identities
11:
| func | period formula |
|---|---|
| sin(ax) | period = |
| cos(ax) | period = |
| tan(ax) | period = |
ANS:
-
a: determines amplitude
b: affects the period
c: and b affects the phase shift -
phase shift simply refers to the angle
or any equation in a trigonometric function()
a)
- any number added or subtracted from the variable is ignored when finding period
any number being multiplied to the variable is divides it in period e.g.has a period of , has period of (since ) has is period of normal
iftrigonometric function have even exponential power, the period becomes half, both have period of
a)
since
- Frequency of a trigonometric function is simply the reciprocal of its period
a)
- Amplitude is the constant multiplied with the trigonometric function and is not negative
have no amplitude, their amplitude does not exist
a)-3
a)4
a)
12: Applications of trigonometry
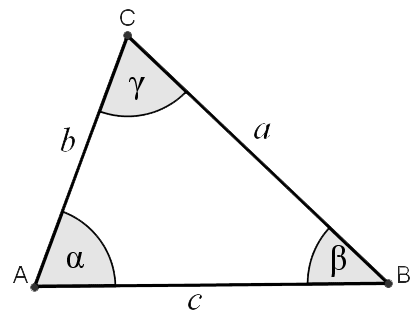
| Law of Sines | Law of Cosines | Law of tangents |
|---|---|---|
| Sine | Cosine | Tangent |
|---|---|---|
| where | ||
| Two sides and included angle | one side and two angles | three sides are given |
|---|---|---|
a)
a)1cm
a)3, 4, 5
b)5, 12, 13 c)6, 7 ,16 d)none
| Type | Angle Condition | Description | Side Relation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | All angles < 90° | Every angle is sharp or narrow | All sides follow a² + b²> c² |
| Obtuse | One angle> 90° | Contains one wide angle | a² + b² < c² |
| Right | One angle = 90° | Contains one perfect right angle | a² + b² = c² (Pythagorean) |
| Oblique | No 90° angle (either acute or obtuse) | A general term for non-right triangles | Covers acute and obtuse |
| where |
13: Inverse Trigonometric Functions
a)
since
a)cannot be calculated
a)5
a)
since
- if asked to express one trigonometric function in terms of other, draw a triangle use that,
| sin | cos | tan |
|---|---|---|
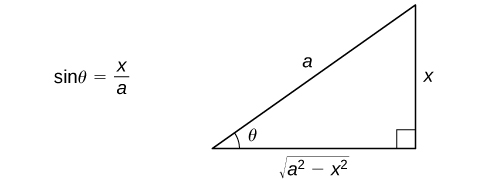 |
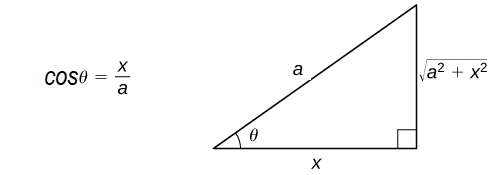 |
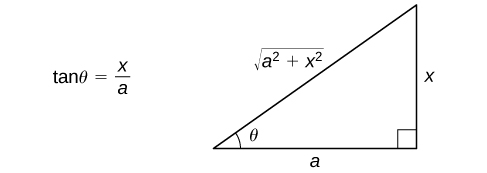 |
| base= |
perp. = |
hypo. = |
a)
a)
Part 2
1: Function & Limits +
| Injective(one to one) | every elements of A maps to only one element of B |
| surjective (onto) | all elements of B are mapped by A, multiple |
| bijective | both |
-
vertical line test determine if a graph is a function or not
- if intersected at two points it is not a function
-
Functions:
- Even:
graph is symmetric with respect to y-axis - Odd:
graph is symmetric with respect to origin
- Even:
-
if
its called involution and give same results for same value of all values of x e.g. -
simplify a fractional limit by taking the derivative of numerator and denominator separately, called rule of De l
Hospital $$\begin{align*}&\text{if f(a) and g(a) are equal to zero \quad } \ & \lim_{x \to a} \dfrac{f(x)}{g(x)} =\lim_{x \to a} \dfrac{f'(x)}{g'(x)}\end{align*}$$ Evaluate the limit:.
a)0
b)undefined c)6 d)3
-
Important:
-
-
-
Vertical asymptotes: in a rational functions
when the equals zero while the does not, if both are zero its a hole -
find inverse by isolating the
and then replacing with and with
a)
- In functions with limit of
, compare the degrees of the numerator and denominator - if degree of denominator > numerator (rational function): limit is 0
- if degree of denominator = numerator : limit is ratio of leading coefficients
- if degree of denominator < numerator (irrational function): limit is
or undefined
a)
| function | value |
|---|---|
| = |
|
| = |
|
| = |
domain and range
- typically domain is represented by
and range is represented by - linear functions:
= 0 have domain and range of R - functions with
here can never be negative so, range is and domain (except ) is all real numbers R only has domain of positive integers
What is the range of the function? - functions with
a)
b) c)all real numbers d)
- Domain and Range of
are Range And Domain of its inverse respectively - in linear and rational functions
, domain is excluding number that makes the function irrational
and range has a shortcut if numerator and denominator have linear polynomial functionsthen exclude ratio of coefficients of x from range e.g. or then Range = or or
2: Differentiation and Derivatives
- if a third variable is present, don't use chain rule, simply do
, now differentiate separately the numerator and denominator with respect to the third variable and divide
a)
-
For implicit function:
-
important
-
has - max. value =
- min. value =
- max. value =
-
order of derivative is highest derivative in the equation
has highest order of 3,
degree is the highest power of x, which in this case is 2 -
a function is:
- increasing if
- decreasing if
- increasing if
a)
| name | ||
|---|---|---|
| product rule | ||
| quotience rule | ||
| reciprocal rule | ||
| power rule | ||
| simple | inverse | hyperbolic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sin | |||
| Cos | |||
| Tan | |||
| Cot | |||
| Cosec | |||
| Sec |
ANS = 0
a)
a)
Rate of change of circumference of circle =
Circumference =
Area of circle =
- LOOK FOR RELATOON BETWEEN MACLAURAN AND GEOMETRIC SERIES AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAH
3: Integration
- for any integral limit of form
- in
a and b are range of - Integration cancels out der uivative:
simply put upper and lower limit:
- if we have
- if upper limit is a variable
and lower limit is a constant
- order: highest derivative in an equation
- degree: power of the term with the highest order
a)
has same derivative and integral
a)
4: Analytical Geometry
-
To determine the unknown point in a parallelogram ABCD, D is equal to sum of its adjacent sides A and C, subtracted by B:
-
a linear equation of two variables represents a line i.e.
- two lines are coinciding if their slopes and
or intercept are equal
| thing | formula | explainations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance | distance between two points | |||
| midpoint | the point in the middle of 2 points | |||
| division of line internally | P is the position vector of the point | !center | ||
| division of line externally | P is the position vector where of the point | |||
| distance between point and line | where |
|||
| slope | the tangent of inclination(θ) | |||
| Centroid of triangle | !center | |||
| in-center of a triangle | where |
from bisector of the angles | !center | |
- slope of horizontal line is
or and of vertical line or undefined - if two lines are perpendicular then
if two lines are parallel then - for three collinear points
- if slope of two lines AB and BC are equal, then A, B and C are co-linear
- in
, x is the distance from y-axis and vice versa
- if in the equation of two lines coefficients of
, and coefficients of are equal then they are parallel a₁=a₂ and b₁=b₂ - Position of a point
relative to a line
- similarly position of a line
relative to axes
- if axis
is shifted through then new axis $$\begin{align}
(X,Y) = (x-h,y-k) \
\
\text{or} \quad (x,y) = (X+h,y+k)
\end{align}$$
in other words, a pointshifted through point , becomes - three lines
are concurrent if
- angle between two lines having selopes
, from to going counter clockwise(arrow strikes )
represents two lines through origin, they are
they are perpendicular if
- the angle between them is:
- pair of lines perpendicular to
are given by
5: Linear Inequalities and Programming
- if an equality
or its associated equation which represents the line, if the equations includes then this line is included otherwise its shown as dotted - a function being maximized or minimized is an objective function
- the solution which maximizes or minimizes a function is called an optimal solution
- feasible regions, region restricted to first quadrant
- optimal solution only exists in feasible region
- intersection of two boundary lines is a corner point if its is in feasible region
- four symbols of inequality
- the corner point satisfies both inequalities, and can be obtained by solving the associated equation of both lines
6: Conic Section
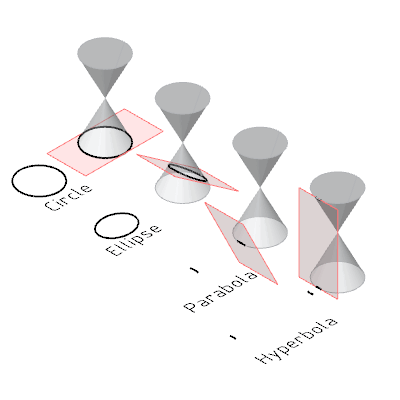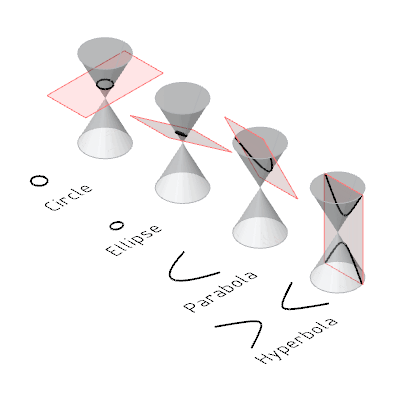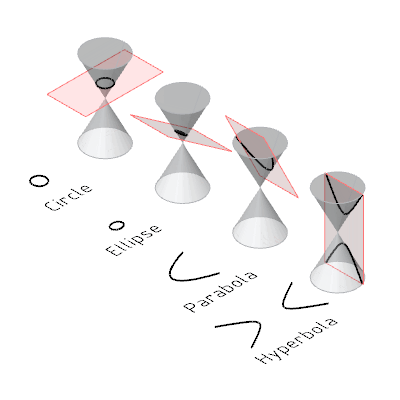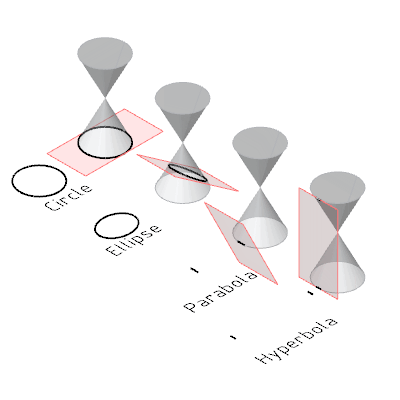
- Degenerated conic:
- a point is a degenerated circle or ellipse (plane parallel or at angle not equal to angle of cone)
- a straight line is a degenerated parabola (plane at angle equal to cone)
- two intersecting lines are a degenerated hyperbola (plane is perpendicular to the cone)
- eccentricity;
is a positive constant, and if
- at maximum, two conic can intersect each other at 4 points, min at 0 points
- determine the conic
if
- any point that lies on a line or conic, satisfies its equation, this core concept is used to solve many MCQs b y back solving
circle:
&\text{General Equation: \quad }Ax^2 + By^2+ 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 \
&\text{Standard Equation: \quad}r^2=(x-h)^2 + (y-k)^2 \
\end
if values
- while solving any MCQ, make sure
are equal to - if radius = 0 then its a point circle
- no
term (product of x and y) is present in equation of circle - if
then circle touches x-axis
ifthen circle touches y-axis
ifthen circle touches both axes
a)X-axis
- length of a chord
, where d is distance of midpoint of chord from center - circle is a special form of ellipse when minor and major axes are equal
- Position of a point
relative to a circle is done by putting point in equation of circle(standard or general)
- to find the quadrants the circle passes though
1.) find center, this will give one quadrant
2.) find radius, compare with the distance of origin from axes, the second quadrant will be the one, which is less than radius
a)I and II
- Circle passes through
- all 4 quadrants if
is negative - 3 quadrants and origin if
is zero
- all 4 quadrants if
tangents
- to find tangent to a curve at any point
, replace
- or take derivative and separate
and then put - length of tangent of circle from
is done by putting in equation of circle and taking square root
CO-EFFICIENT OFAND MUST BE ONE
from the point P(-1,2)
Parabola:
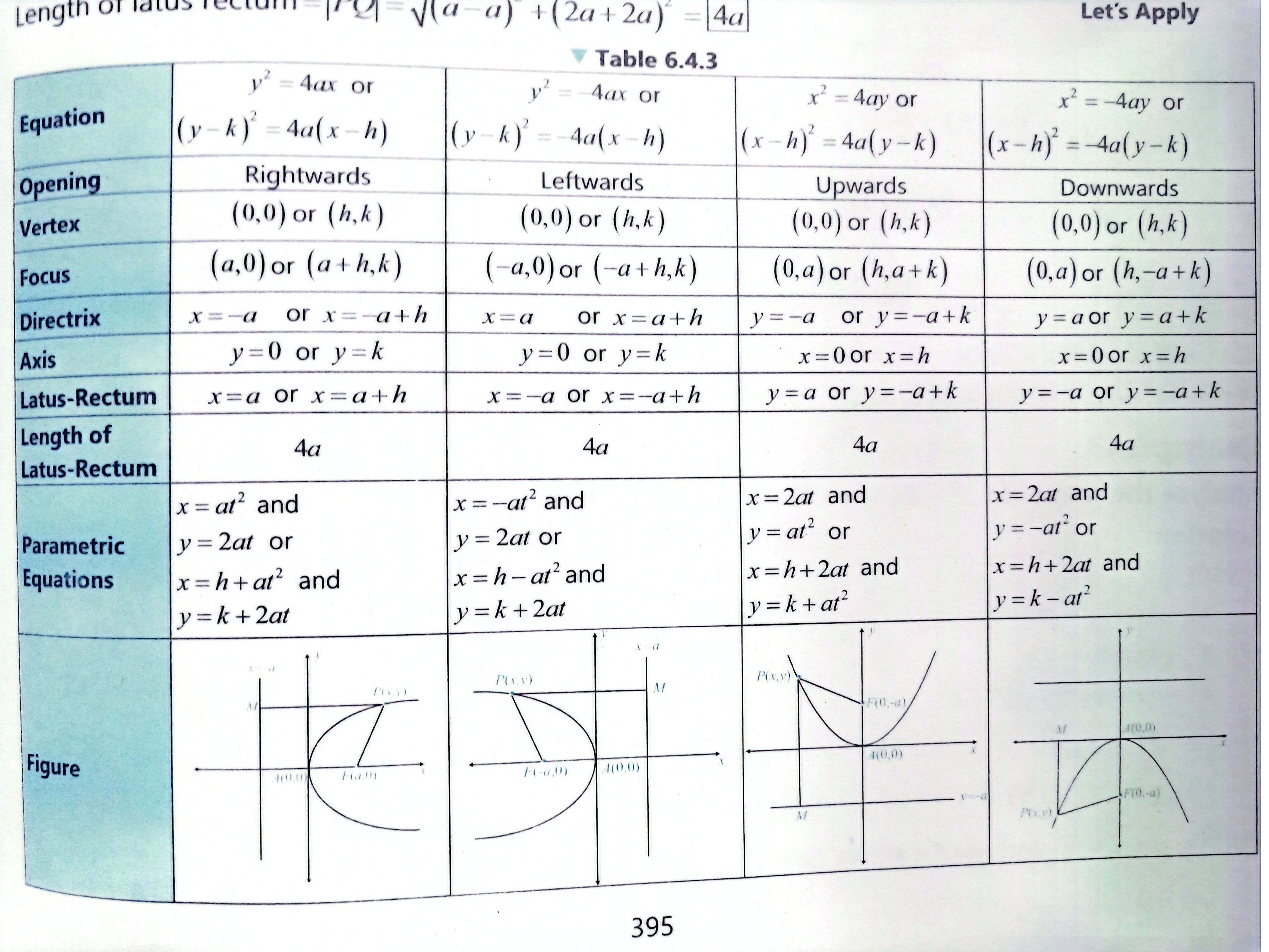
-
the parabola opens where the term with degree 1 points; x-right, -x-left, y-up, -y-down
-
is called the focal length -
for form
-
line
is tangent on parabola if: -
in any equation:
, the term is the axis -
for any equation of form
solve it by completing square
Ellipse:
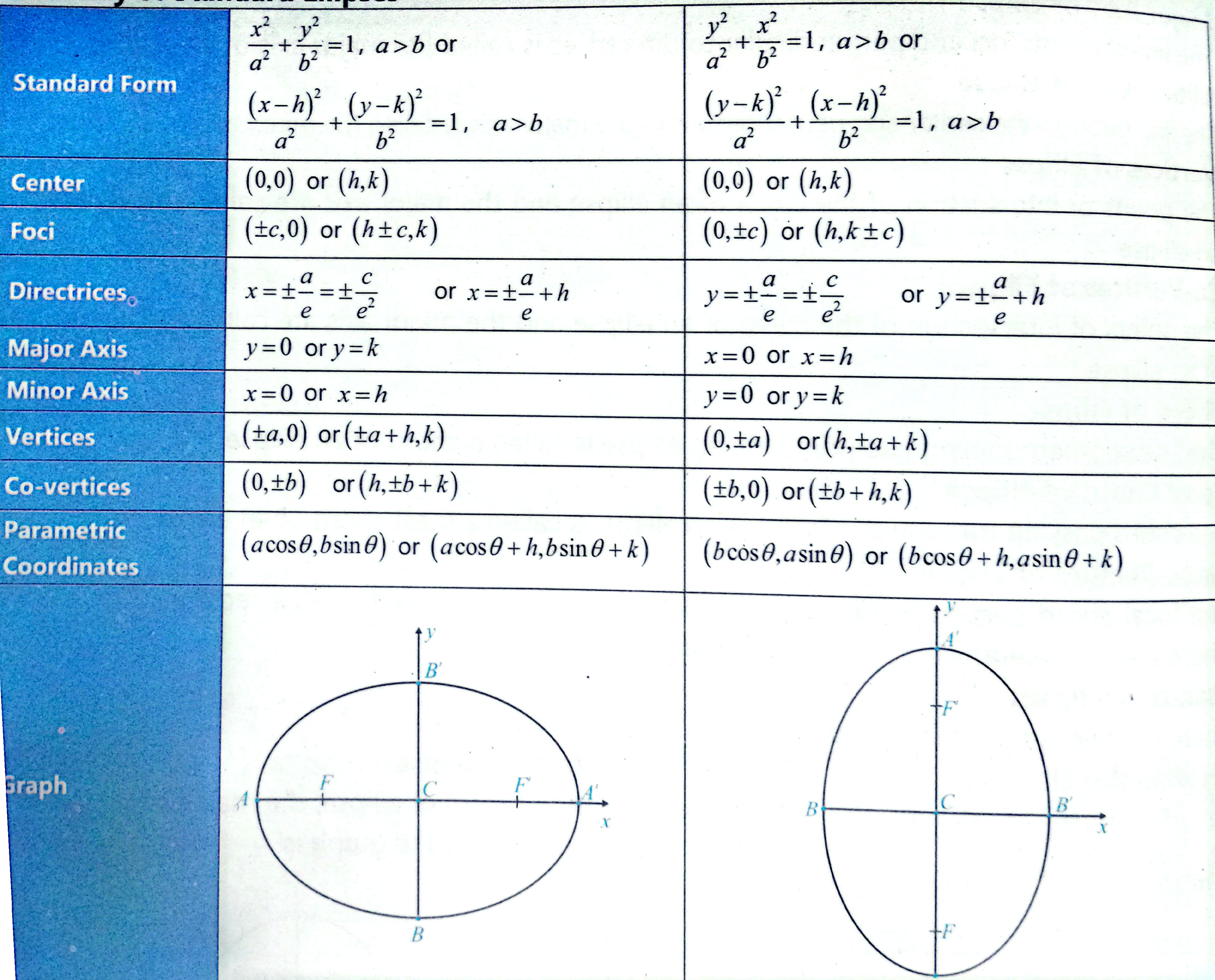
: length of major axis : length of minor axis distance between center and foci: distance between foci - semi major axis means only
, as in half of major axis - eq. directrix: x or y = ± a²/c
- distance b/w directrices: d= 2a²/c
- Area:
- Perimeter≈
- focal parameter: distance between focus and directrix:
- in standard form of ellipse
if certain conditions are met, of A and B, the bigger can be a² and smaller can be b²
the largest circle inside will have radius equal to semi minor axis = b,
Hyperbola:
- product of distances of foci to any perpendicular is
- hyperbola is along the axis which is positive in the equation
- symmetric on both axes
- Foci:
- distance between foci: 2ck
- Directrices =
- Length of latus-rectum: =
- Length of traverse axis(where vertices lie): 2a
- Length of conjugate axis(where co-vertices lie): 2b
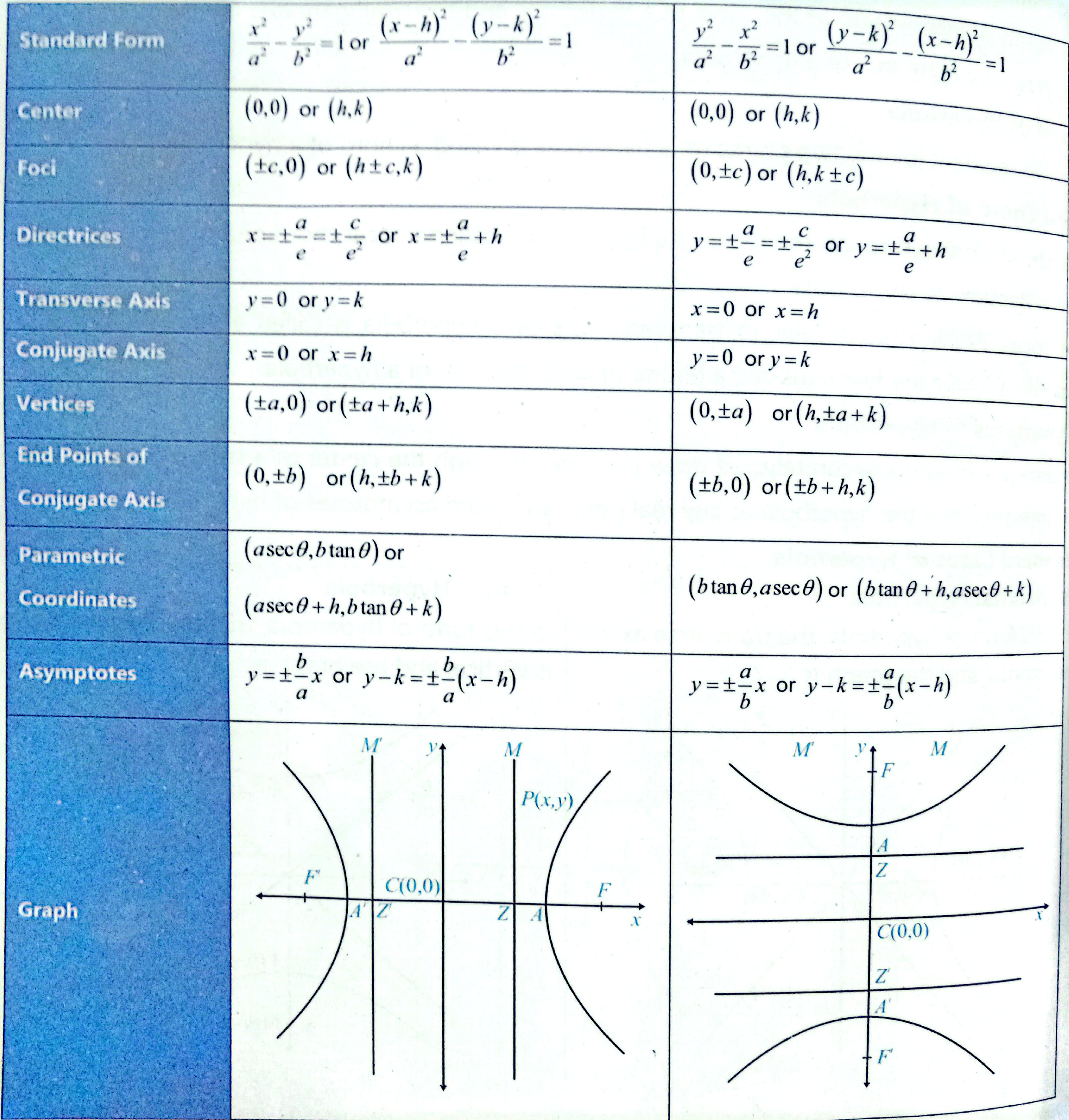
Center = (2,-1)
Vertices(∓(a+h), k) = (∓(3+2),-1)
Co Vertices(∓(b+h), k) = (∓(4+2),-1)
Foci (∓(c+h),k) = (∓(5+2),-1) ;
- for asymptotes simply replace the 1 with 0 and solve for y
a)
- In rectangular hyperbola
where c is a constant - its eccentricity is always
- their asymptotes are perpendicular
7: Vectors
- sum of vectors forming a closed loop is zero
a)(10,10,10)
- for a triangle sum of its sides as vectors is zero $$\underline{u} + \underline{v} + \underline{w} = 0$$
or sum of its any two sides, is equal to the third$$\underline{u} + \underline{v} = \underline{w} $$
a)4
- line segment from origin to point is a position vector
- from point to point is a vector
- if two vectors are perpendicular and you need to find one of their coordinates, set their dot product equal to zero and solve
a)
- projection of B on A where
is the angle b/w them is: = component of B along A =
a)-1
- orthogonal: if two curves are perpendicular
- for any vector, where
are its angles with corresponding axes - For any two parallel vectors
and , the ratios of coefficient of corresponding components are equal
i.e.
a)4
- a vector
is - is
units away from z-axis - is
units away from y-axis - is
units away from x-axis
- is
a)5
-
Direction cosines of a vector are the components of its unit vector
- e.g.
has direction cosines of and
- e.g.
-
Scalar Triple Product:
- its zero if the vectors are co planar
- it gives the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the three vectors.
a)30
a)