Part 1
1: Physical Quantities -+
- 1 Dyne =
Newton; dyne is from CGS system and Newton from SI - Uncertainty error affects precision, not accuracy
- Least Count measures precision
- Precision: How detailed a measurement is
Accuracy: How correct a measurement is - Young's Modulus, Pressure, Stress and Energy Density have same dimensions
| Quantity | Definition | Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Young's Modulus | Measure of stiffness (stress/strain) | M L⁻¹ T⁻² |
| Pressure | Force per unit area (F/A) | M L⁻¹ T⁻² |
| Stress | Force applied per unit area (F/A) | M L⁻¹ T⁻² |
| Energy Density | Energy per unit volume (E/V) | M L⁻¹ T⁻² |
| Shape | Volume | Perimeter | Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere | (4/3) π r³ | N/A | 4 π r² |
| Circle | N/A | 2 π r | π r² |
| Square | N/A | 4a | a² |
2: Vectors -
- resolving = splitting into components
- minimum no. components = 2
- maximum no. components =
- there can be a maximum of 3 rectangular components
- Modulus = Magnitude =
- angle with
- west is on the left, east is the right
| Operation | Trigonometric Formula | Component Formula | Perpendicular | Parallel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dot Product | Max if |
|||
| Cross Product | Max if |
- if sum of two forces of same magnitude is equal to the individual force, the angel
- projection of B on A where
is the angle b/w them is: = component of B along A = = - Resultant of two vectors
with same initial at an angle is: - among unit vectors,
if either of any among these pairs is -ve then simply separate it and solve
e.g.
a)0
- dot product and cross product of two vectors are equal at
3: Motion and Forces+
- state of motion and rest are relative
- acceleration of a free-falling object remains constant, unless obstructed by drag force of medium
- Laws of Motion show relation between a body, the force acting on it and the resulting motion
- net force on a body at rest or in uniform motion is zero
- in circular motion speed can be constant while acceleration
| formulae | formulae | formulae |
|---|---|---|
a)4.9m
it took 1 sec to go up and 1 sec to come down,
- gravity is stronger at poles than at equator
- projectile formulae
| Height | Range | Total time | time to reach maximum height |
|---|---|---|---|
- Height and Range of a projectile become equal at angle
- The range of project at
and at are same if e.g. at or - at maximum height, the horizontal acceleration becomes zero in projectile motion
4: Work and Energy-+
- Work = Energy
a)79.6 W
- Work = Change in energy =
a)54J
- Torque
a)73
- Power of a motor torque:
is angular velocity =(impulse = change in momentum) - centripetal force does no work (angle between force and displacement is 90,
) - 1 horse power = 746 watt
joules - K.E =
relation of K.E and momentum
| Energy | formula |
|---|---|
| P.E | |
| K.E | |
| Work |
-
Energy units: Joules, Kilowatt-hour, electron volt
-
mass of earth:
-
radius of earth:
-
: to escape from gravitational field
: to enter an orbit
-
work done for the same mass of object is dependent on the height reached or distance covered
a)1:2
- Friction: opposition force
where is the coefficient of friction(unitless) and is the normal force between the surfaces - Friction has unit of newton
5: Circular Motion-+
| quantity | Translational | Rotational | relation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| displacment | ||||
| velocity | ||||
| acceleration | ||||
| mass/moment of inertia | ||||
| momentum | ||||
| force/torque | ||||
| Kinetic Energy |
a)2 times
If the radius of an object moving in a circle is halved, its moment of inertia about the center of the circle decreases by a factor of four
is length of the curve, is the radius OR - Centripetal Force
- unit of linear momentum =
- unit of angular momentum =
- Angular momentum is constant in both speed and direction for: constant speed
- Angular momentum is constant in only direction for: varying speed
a) Her angular velocity decreases because her moment of inertia increases.
b)Her angular velocity remains constant as angular momentum is always conserved.
c)Her angular velocity decreases because her moment of inertia decreases.
d)Her angular velocity increases because her moment of inertia increases.
| shape | moment of inertia | |
|---|---|---|
| rod | 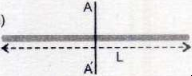 |
|
| Hoop/ring | 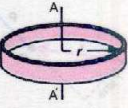 |
|
| disc | 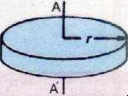 |
|
| sphere | 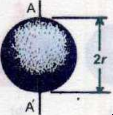 |
- pseudo force: arises without any contact e.g. Centrifugal force
- Apparent weight
falling down:= original weight - upward force
going up:= original weight + extra force
6: Fluid Motion-
- 1 atm = 101325 Pa = 760 mmHg = 760 torr
- Stroke's Law:
- Terminal Velocity:
- Terminal velocity of a body is constant and its maximum velocity in that medium
| Blood Pressure | Relatively | Flow | in Healthy person (in torr or mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic | High | Turbulent | 120 mm Hg |
| Diastolic | Low | Laminar | 80 mm Hg |
| written as 80/120 |
-
Equation of continuity:
-
pressure of fluid in pipe is:
| Theorem | Derived from |
|---|---|
| Bernouli's theorem | conservation of energy |
| Equation of Continuity | conservation of mass |
| theorem | Formula | effect/definition | relates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke's Law | Drag force on a spherical body | ||
| Torricelli | velocity of water(speed of efflux) from a hole, where Δh is the height from hole to surface | ||
| Venturi | Where space is narrow in a pipe speed of fluid is high, pressure will be low Speed and Pressure and | ||
| Bernoulli's Effect | Where speed of fluid is high, pressure will be low | ||
7: Oscillations
- in vibratory motion total energy remains constant i.e. sum of K.E and P.E
- total energy in SHM = K.E + P.E =
(A is amplitude)= constant in perfect system - Gravity of Moon =
its 1/6th times earth gravity i.e.
a)6 sec
- Apparent gravity
- descending :
: decreased - ascending :
: increased
- descending :
a)
a)increased
| Extreme Position | Mean Position |
|---|---|
| K.E is minimum | K.E is maximum |
| P.E is maximum | P.E is minimum |
| Velocity is minimum | Velocity is maximum |
| Acceleration is maximum | Acceleration is minimum |
| Displacement is maxmimum | Displacement is minimum |
| system | Time period | P.E | K.E | accleration | Angular Freqeuncy | mass and amplitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | mass does affect time period |
|||||
| Pendulum | do not affect time period |
a)doubled
- vibratory motion is simple harmonic if angular velocity
is uniform - projection of a body moving in a circle where
is radius of circle and is current amplitude
| displacement | velocity | acceleration |
|---|---|---|
- Initial position
: mean position : extreme position
a)0⁰
- Hook's law:
where is the force constant - force constant has same unit as surface tension:
- force constant has same unit as surface tension:
- second pendulum: pendulum with a time period of 2 seconds or frequency of
hertz
a)1m
a)1 sec
- System under forced vibrations is Driven Harmonic Oscillator
8: Waves
a)
| Doppler effect | Shift | Wavelength | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| moving towards an observer | blue shift | decreases | increases |
| moving away from an observer | red shift | increases | decreases |
- speed of sound
and **does not directly depend on pressure
and
a)1132°C
-
sound has double speed in air at 819°C than it does at 0°C
-
a)2 times
taking molar mass instead of density as they are proportional,
-
rarer to denser:
- reflection: 180 phase shift
- refraction: towards normal;
increases, increases
-
denser to rare:
- reflection: no change in phase angle
- refraction: away from normal;
decreases, decreases
-
Waves are Slow in Shallow(rarer) water and faster in deep (denser) water
- going from shallow to deep:
increases, increases - going from deep to shallow :
decreases, decreases
- going from shallow to deep:
-
Newton: movement of sound through air is isothermal (same temperature)
Laplace: movement of sound through air adiabatic(no heat transfer out of system) (correct hypothesis) -
Sound intensity: power per unit area =
= Decibels
Decibels is a logarithmic scale -
waves transport both energy and momentum
-
-
monoatomic gases have the highest
at 1.67 -
Constructive interference:
- In phase
- path difference =
-
Destructive interference:
- Out of phase
- path difference =
-
Entering from one medium to other
Frequency remains same and is independent of medium
Velocity and Wavelength are changed -
in open pipe:
- at end anti-node is formed
- both odd and even harmonics can be made and hence contains more harmonics
-
in a closed pipe:
- in closed pipe: at end node is formed
- only odd harmonics are present and hence contains less harmonics
-
ratio b/w fundamental frequencies of open and closed end pipes: 1:2
-
whether you change the frequency or wavelength, the speed of sound in a medium remains same
-
speed of sound increases in air by
per 1 Kelvin increase -
in any wave, crust and trough are separated by half a wave:
-
Ultrasonic: >20kHz
-
beats per second:
- difference of interfering waves=
where is greater
- difference of interfering waves=
a)100Hz
- Applications of super-position:
- Interference:
same; direction=same - Beats:
=small differences; direction=same - Stationary waves:
=same; direction=opposite
- Interference:
- We can listen a maximum of 10 beats per second
-
\text{ loudness }\propto \text{ amplitude }\end{align}$$
9: Optics
- light rays directly from source are unpolarized and contain both magnetic and electric fields
- no polarization in longitudinal waves
- E.F and M.F are always perpendicular
- a slit produces a bright fringe at the center
- in refraction: frequency remains unchanged
- light rays from bulb are spherical
- sky is blue due to light scattering
| Refraction | wavelength | bend |
|---|---|---|
| denser to rarer | decreased | towards normal |
| rarer to denser | increased | away from normal |
10: Optical Instruments
- The final image produced by a compound microscope is virtual, inverted, and magnified
11: Heat and Thermodynamics
- Adiabatic: No heat exchange occurs
Isothermal: at constant temperature
Isobaric: at constant pressure - Internal Energy: Sum of all energies of molecules of system
- Work done on an isothermal gas with volume change:
a)
- entropy is a measure of randomness/disorder -
- the more evenly/uniformly distributed heat is in the system, the greater the entropy
- every natural process moves towards greater entropy(earth quake, floods, melting of ice, etc)
- SI unit:
- Efficiency of Carnot engine:
; temperature in kelvin - Laws of Thermodynamics:
- First Law: energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
- Second Law: the entropy of an isolated system always increases over time, indicating a tendency towards disorder or randomness.
- Third Law: entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero (0 Kelvin) is zero, meaning a system at absolute zero is in its most ordered state
Part 2
12: Electrostatics+-
- if two similarly charged bodies are touched, charged is transferred so that both of them have equal charge e.g. after touching a 1C and 3C body they both have 2C
- in a medium of permittivity
force between two charges becomes - a static charge possesses only electric field, but moving/flowing charge possesses both magnetic and electric fields
| Quantity | effect upon addition of a dielectric in a capacitor |
|---|---|
| Voltage | decreases |
| Electric Intensity | decreases |
| Capacitence | increases |
| Charge | constant |
- in all equations charge is assumed to be positive, it maybe negative but it is preferred positive, if told to chose only one, choose positive
if both can be chosen, chose both - capacitor is also called the condenser
- in a capacitor, if charge is 100%, then current is zero, current is 100% if charge is zero
a)Infinity
- charge is quantized, multiple of e =
| coulomb force b/w two charges | ||
| Capacitence | ||
| Energy stored in capacitor | ||
| Electric Intensity and Voltage | ||
| Electric potential due to a charge | ||
| Electric Intensity | ||
| Electric Flux |
- its
seconds for a capacitor to charge up to 63% of its capacitance - energy of capacitor in parallel is more than ones in series
- capacitor holds charge due to electric fields and charges due to electrostatic induction
-
charged is quantized, any multiple of
(charge on one electron and minimum charge on a body) -
Capacitors in parallel:
if same
Capacitors in series:
if same -
if a capacitor has charge Q, then one plate has
and the other i.e. they store - equal and opposite charges
-
direction of electric field outside:
13: Current Electricity+-
| Quantity | Unit | relation |
|---|---|---|
| Conductance | mho/siemen | |
| resistance | ohm | |
| Conductivity | mho |
|
| resistivity | ohm |
- drift velocity ≈
- H = heat =
- Resistors in series:
if same
Resistors in series:
if same
| current and Charge through an area | |
| resistence, length, area and |
|
- if wire is stretched to n times(its orignal length)then resistence becomes $$R'=n^2R$$
B B ~={red}R=~ O Y ~={green}G=~ ~={blue}B=~ ~={magenta}V=~ ~={yellow}Y=~ W
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| Power | ||
|---|---|---|
| for series | Higher resistence consumes more power | |
| for parallel | Lower resistence consumes more power | |
- If E is emf of cell, r is internel resistence and IR=V the terminal voltage$$\begin{align*}E = IR + Ir \I = \dfrac{E}{R+r}\end{align*}$$
14: ElectroMagnetism+-
-
current through two parallel wires
- if same direction: attract
- if opposite direction: repel
-
permeability of free space:
-
inductance of inductors is added similar to resistors
| thing | guy |
|---|---|
| magnetic effect of current | Oersted |
| quantity | units | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Flux | ||
| Flux Density Magnetic Field Strength Magnetic Field Induction |
| Magnetic Field Inside a solenoid | not affected by radius(area of coil) | |
| Magnetic Field at a distance r from wire | ||
| Magnetic field at the center of a coil | ||
| Force on current carrying conductor | direction using right hand palm rule | |
| Emf by a rotating coil in M.F | ||
| Torque on coil in magnetic field | in radial magnetic field, its only NIAB | |
| force on charge in magnetic field | no force on stationary charge, no work is done no change in K.E |
|
| force on charge in electric field |
a)
- Lorentz Force = Vector sum of magnetic and electric forces
= - Unit of magnetic dipole moment:
| law | based on law of |
|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Induction | Conservation of energy |
- a charge moving in a straight line perpendicular to a magnetic field moves in a circle
- a charge moving at an angle between 0 and 9 moves in an elliptical path
- if field into the page charge(+ve) will move clockwise (using right hand rule)
- a charge in an electric field moves towards the oppositely charged site
- galvano meter only detects currents, not measure it
15: ElectroMagnetic Induction-+
- Transformer only works for A.C, not for DC(dry cell, battery, etc)
- ohm law(V=IR) does not apply on inductors only resistors
- Induced emf depends on change of flux
but magnitude of induced emf depends on rate of change of flux - Step up:
Step down: - A.C generator: Slip Rings
D.C generator: Split Rings - dynamo(A.C generator) converts: mechanical energy into electric
- Induced emf sometimes acts as back emf
- Induced emf does not depend on resistance of coil but induced current does
- if there are x cycles in A.C of f hertz, then
current change direction 2x times
current reaches max. 2x times
| Energy stored in Inductor/magnetic field | ||
| emf induced in rotating coil (A.C generator) |
when flux( emf( |
|
| Mutual Inductance Self Inductance |
unit is henry |
16: Alternating Current+-
- wavelength(
) of x-rays is in order of
| Reactance( |
device | lead and lag( |
Power Factor( |
|---|---|---|---|
| ~={green}Inductor=~ | ~={green}current lags=~ by |
||
| ~={blue}Capacitor=~ | ~={blue}current leads=~ by |
||
| R | Resistor | current and voltage are in phase |
|
- CL circuit is an oscillatory or rejecting circuit
| circuit | impedance( |
phase difference |
|---|---|---|
| RL | ||
| RC | ||
| R | ||
| RLC |
| thing | definition |
|---|---|
| Carrier Wave | High frequency wave |
| Modulation Signal | Low frequency wave |
| modulated carrier wave | resulting wave from modulation |
| thing | definition | transmission freq range |
use | flaw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulation | combining high freq radio wave and low freq signal | |||
| Amplitude Modulation | combining amplitude of high freq. and amplitude of low freq. | 540 kHz to 1600 kHz | long range | easily distorted |
| Frequency Modulation | combining freq. of high freq. and amplitude of low freq. | 88 MHz to 108 MHz | immunity to electrical disturbance | small range |
- RLC circuit behaves like an~={green} RC=~ circuit at ~={green}low frequency=~
RLC circuit behaves like an ~={blue}RL=~ circuit at ~={blue}high frequency=~
RLC circuit behaves like an R circuit at resonance frequency( power factor = 1) - at resonace frequency(
):
~={red}resonance frequency:=~ - In series at resonance freq.: impedance is min.,power is max
- In parallel at resonance freq.: impedance is max., power is min
Radio waves have a prominent wave nature
Gamma rays have a prominent particle nature
as wavelength decreases/freq. increase particle nature increase
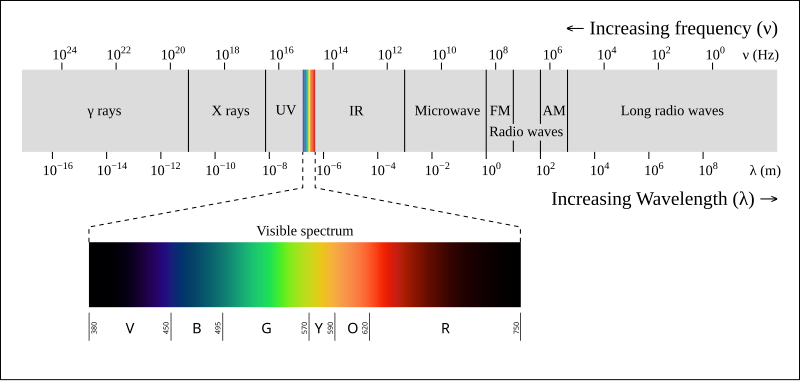
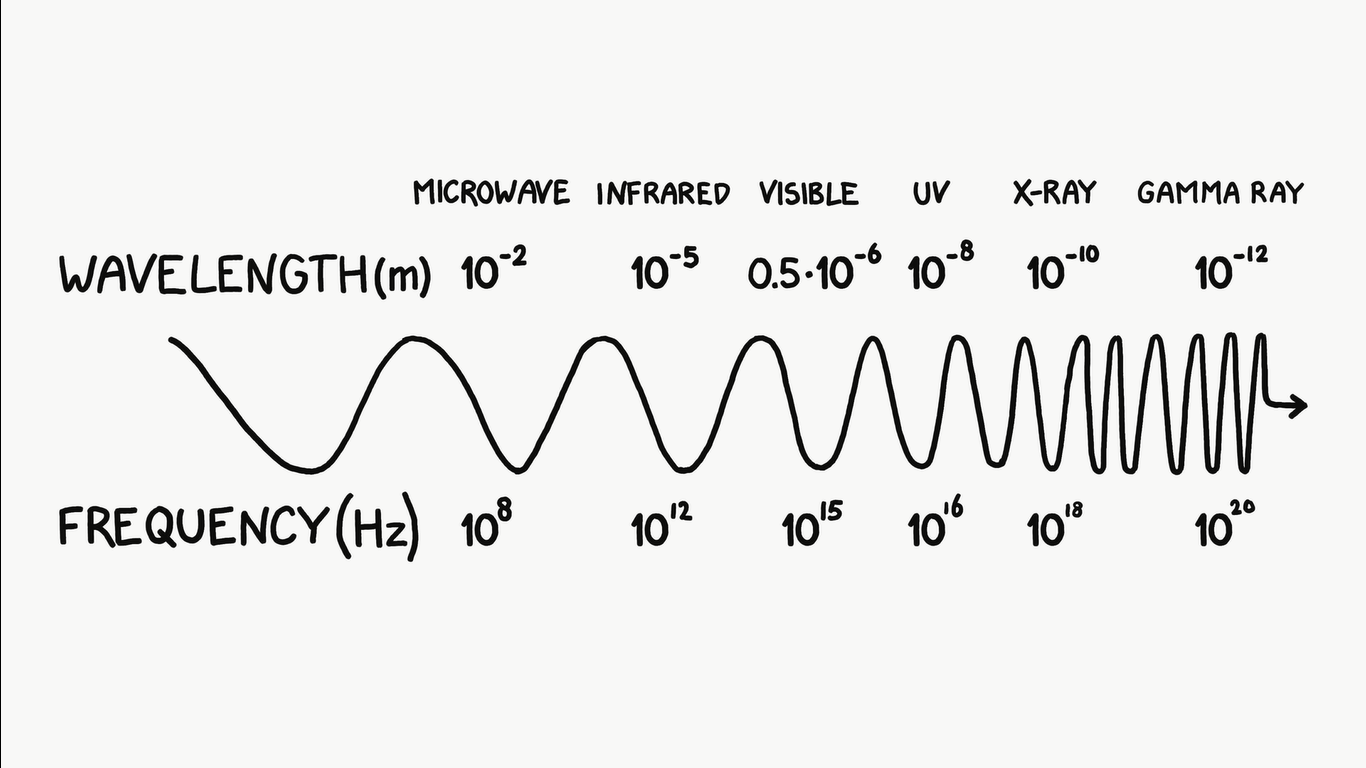
- static charge: only E.F
moving charge: both E.F and M.F but no E.M wave
accelerating charge: changing E.F, M.F and E.M waves - choke is used to control flow of A.C
- Maxwell's formula for speed of light
where:
is the permeability of free space is the permittivity of free space
17: Physics of Solids-+
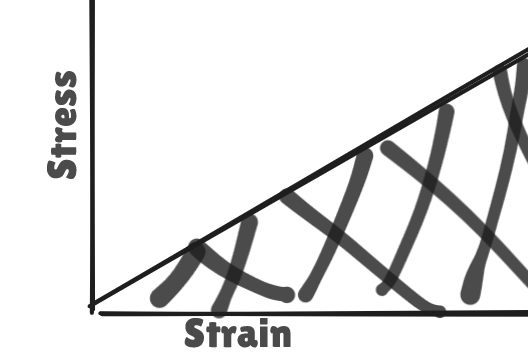
- hook's law is constant so wherever it is obeyed the graph between stress and strain will be a straight line
- strain is :
so doubling the length will have a strain of 1 - resistivity of conductors is in the order of
| thign | formula | unit | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress | |||
| Strain | no unit | doubling the length will have a strain of 1 |
| modulus | energy |
type | formula | note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young's | linear | Solid only and infinity for perfectly rigid body | ||
| Bulk's | volumetric | solids and gases, infinity for perfectly rigid body |
||
| Shear | angular | only solid |
- hence steel has more elasticity than rubber
- Area of Stress-Strain curve has units of energy density
| type | charge carrier | impurity |
|---|---|---|
| N-type | free electrons in conduction band | penta-valent |
| P-type | holes in valence band | tri-valent |
| material | in magnetic fields | behavior | examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimagnetic | weakly repelled | no unpaired electron | copper, bismuth, water, antimony |
| Paramagnetic | weakly attracted | some unpaired electron so magnitizes momentarily | aluminum, platinum, oxygen |
| FerroMagnetic | strong attracted | many unpaired electron and retain magnitized state | iron, cobalt nickle |
- at 0K conduction band of semi-conductors is empty and valence band is filled and acts as an insulator
- bond length of nickle =
- glass is a solid liquid bcz of irregular(liquid) but fixed(solid) relative position of molecules
- Modulus of elasticity relates inversly with temperature
18: Electronics +
- a pn-junction is biased as long as a potential is applied whether current flows or not
| Type | minority charg | majority charge | Dopping | dopping example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-Type | free electrons | holes | Trivalent/Acceptor | |
| N-Type | holes | free electrons | Pentavalent/Donor |
| bias | conventional current/potential) | depletion region |
|---|---|---|
| forward | from P to N | is shortened |
| reverse | from N to P | is widened |
| recitification | diodes | conducting at once | output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| half wave | 1 | 1 | pulsating DC | |
| full wave | 4 | 2 | pulsating DC | |
| center-taped | 2 | 2 | pulsating DC |
- depletion regions increases(reverse bias) and decreases both due to majority charge carriers
- Emitter current> collector current> base current
- AND can be represented by two switches in series
OR can be represented by two switches in parallel
| identification | gates | symbolic |
|---|---|---|
| true only when both are zero | NOR | |
| false only when both are one | NAND | |
| true only on different inputs | XOR | |
| true only same inputs | XNOR |
- OP-AMP can amplify both AC and DC
19: Dawn of Modern Physics
- motion alters space and time
| constants | value | symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Stefan's | ||
| Wien's | ||
| Planck's |
- Relation between energy of emitted photons and temperature:
\text{Frequency of emitted photon} \qquad \propto \qquad & \dfrac{1}{ \text{Wavelength}} \propto \qquad\text{Temperature}
\end
| at high(relativistic) speeds of observer and as speed increases |
at speed of light | become double when v= |
becomes half at |
|---|---|---|---|
| time increases | stops | ||
| length decreases | becomes zero | ||
| mass increases | becomes infinity |
-
no object can travel faster than
and all forms of radiation/photons travel at -
there is no absolute standard of motion
-
-
-
a)1.1 eV
a)4.48eV
| Energy relation | def | Relation |
|---|---|---|
| Mass-energy conversion | ||
| Energy of photon with |
||
| Energy of photon with |
||
| Momentum of photons with |
- rest mass of photon is zero
| thing | formula |
|---|---|
| momentum of photon | |
| debroglie wavelength | |
- Gamma and X-rays: prominent particle nature
IR, Micro, radio waves: prominent wave nature
Photo Electric Effect
20: Atomic Spectra:
-
Wavelength for X-rays in orders of:
-
ionization energy of hydrogen:
-
any color shown on an object is the color not absorbed
a)transmit
21: Nuclear Physics
- muons have same charge as electrons
- mesons : one quark and one anti quark
baryon: three quarks
electrons: a fundamental particle
neutrons are made of three quarks: 2 up, 1 down - up-quarks have
charge - there are 6 leptons
- penetration power:
- humans emit IR
- decay calculation:
a)125g
decayed =
- rate of decay: activity:
a)280 days
- only noble gases are used in GM counters
- forces in nature occur in pairs
- fission of two deuterons, releases 1 neutron
- Fast moving Neutron: K.E> 1KeV
- X-rays are unaffected by magnetic field
- if
-alpha is release:
if
a)Z-3, A-4
if
a)
- at least one alpha and two beta emissions are required for an isotope
| thing | definition | formation | examplpe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| isotope | same atomic number, different mass number | |||
| isobars | same mass number, different atomic number | |||
| isotons | same mass number, same proton number, different neutron | no>:( | ||
| isodiapers | different mass, atomic number, and neutrons |
| thing | unit | old/other unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength of radiations | Becquerel(Bq) one disintegration per second |
Curie(Ci) |
| Effect of radiation Dose (D) = |
Gray (Gy) one joule per kilogram |
Radiation Absorbed Dose (Rad) 1 rad = 0.01 Gy 100 rad = 1 Gy |
| Biological Effectiveness RBE |